The Link Between Fat Oxidation and Liver Health: Understanding the Connection
Introduction
The liver is a vital organ responsible for a wide range of functions in the body, including detoxification, metabolism, and storage of nutrients. One of the key functions of the liver is the breakdown of fats through a process called fat oxidation. Fat oxidation is the process by which fats are broken down into smaller molecules and converted into energy. This process is crucial for maintaining a healthy weight and preventing the buildup of excess fat in the body. In recent years, research has shown a strong link between fat oxidation and liver health. In this article, we will explore the connection between fat oxidation and liver health, and how it impacts overall health and well-being.
Understanding Fat Oxidation
Fat oxidation is a complex process that involves the breakdown of fats into smaller molecules called fatty acids, which can be used as fuel by the body. This process occurs in the mitochondria, the powerhouse of the cell, where fatty acids are broken down through a series of chemical reactions to produce energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This energy is then used by the body for various functions, including muscle contraction, metabolism, and overall energy production.
There are several factors that can influence fat oxidation in the body. These include genetics, diet, exercise, and overall metabolic health. For example, individuals with a high metabolic rate may have a greater capacity for fat oxidation, while those with metabolic disorders such as diabetes or insulin resistance may have impaired fat oxidation. Similarly, a diet high in saturated fats and processed foods can inhibit fat oxidation, while a diet rich in healthy fats, such as omega-3 fatty acids, can promote fat oxidation and overall liver health.
The Connection Between Fat Oxidation and Liver Health
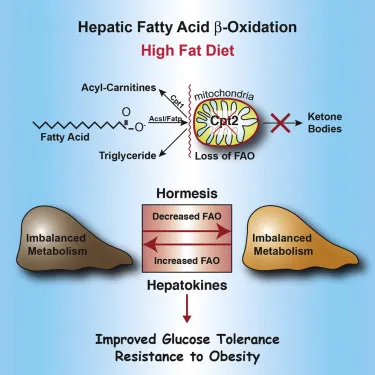
The liver plays a crucial role in fat metabolism and oxidation. It is responsible for processing and storing fats, as well as regulating the release of fatty acids into the bloodstream for energy production. When fat oxidation is impaired, either due to a high-fat diet, sedentary lifestyle, or metabolic disorders, the liver can become overwhelmed with excess fats, leading to a condition known as fatty liver disease.
Fatty liver disease is a common condition characterized by the buildup of excess fat in the liver cells. This can lead to inflammation, scarring, and ultimately liver damage if left untreated. Research has shown that impaired fat oxidation is a key factor in the development of fatty liver disease. When the liver is unable to effectively break down fats for energy, they accumulate in the liver cells, leading to oxidative stress and inflammation.
In addition to fatty liver disease, impaired fat oxidation has also been linked to other liver conditions, such as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and cirrhosis. NASH is a more severe form of fatty liver disease characterized by inflammation and liver cell damage, while cirrhosis is a late-stage liver disease characterized by scarring and loss of liver function. Both of these conditions are associated with impaired fat oxidation and can have serious consequences for overall health and well-being.
Promoting Liver Health Through Fat Oxidation
Maintaining healthy fat oxidation is crucial for promoting liver health and preventing liver disease. There are several ways to support fat oxidation and improve liver function, including:
1. Eating a balanced diet rich in healthy fats, such as omega-3 fatty acids found in fish, nuts, and seeds.
2. Limiting intake of saturated fats and processed foods, which can inhibit fat oxidation and contribute to liver damage.
3. Engaging in regular physical activity, which can improve metabolic health and promote fat oxidation.
4. Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, which can impair liver function and inhibit fat oxidation.
5. Managing underlying health conditions, such as diabetes or insulin resistance, which can impair fat oxidation and increase the risk of liver disease.
By incorporating these lifestyle changes, individuals can support healthy fat oxidation and promote liver health. This can help reduce the risk of fatty liver disease, NASH, cirrhosis, and other liver conditions, and improve overall health and well-being.
FAQs
Q: Can fat oxidation be measured?
A: Yes, fat oxidation can be measured through various methods, such as indirect calorimetry, which measures the amount of oxygen consumed and carbon dioxide produced during fat metabolism. This can provide valuable information about an individual’s metabolic rate and fat oxidation capacity.
Q: Are there supplements that can support fat oxidation?
A: Yes, there are several supplements that can support fat oxidation, such as omega-3 fatty acids, green tea extract, and L-carnitine. These supplements can help improve metabolic health and promote fat oxidation, but should be used in conjunction with a healthy diet and lifestyle.
Q: Can impaired fat oxidation be reversed?
A: Yes, impaired fat oxidation can be reversed through lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing underlying health conditions. By supporting fat oxidation, individuals can improve liver health and reduce the risk of liver disease.
Conclusion
In conclusion, there is a strong link between fat oxidation and liver health. Impaired fat oxidation can lead to the buildup of excess fats in the liver, leading to conditions such as fatty liver disease, NASH, and cirrhosis. By promoting healthy fat oxidation through diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes, individuals can support liver health and reduce the risk of liver disease. Understanding the connection between fat oxidation and liver health is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. By taking steps to support fat oxidation, individuals can improve liver function, reduce inflammation, and promote optimal health.