Exploring How Stress Can Affect Gut Health
Have you ever wondered if the stress you’re experiencing is taking a toll on your gut health? It’s a question that resonates with many of us as we navigate life’s challenges. Stress is an inevitable part of life, but understanding its impact on your body, specifically your gut, can empower you to take steps toward better health.
The Gut-Brain Connection
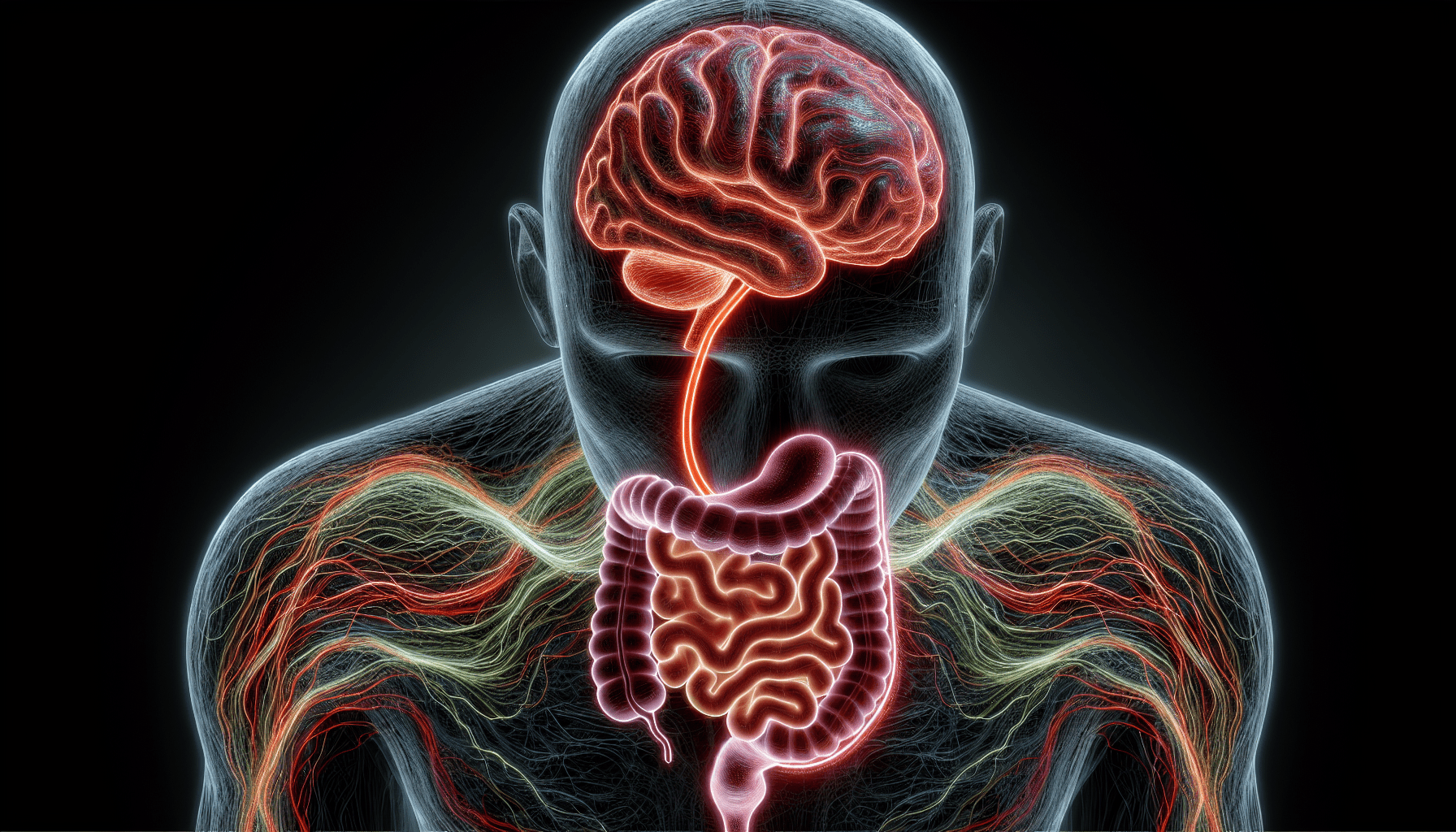
To comprehend how stress can affect your gut health, it’s crucial to first understand the gut-brain connection. This refers to the bidirectional relationship between your central nervous system and the gastrointestinal system. They communicate back and forth, influencing each other in various ways.
The Role of the Vagus Nerve
The vagus nerve plays a pivotal role in the gut-brain connection. It’s a major conduit for signals traveling between your brain and your gut. When you’re stressed, your brain sends signals through this nerve, impacting your digestive processes. The vagus nerve helps regulate the parasympathetic nervous system, which is often referred to as the ‘rest and digest’ system. When stress takes over, it can inhibit this regulation, leading to digestive disturbances.
Microbiota as a Communicator
Not only does your nervous system communicate with your gut, but so does your gut microbiota. These trillions of bacteria residing in your intestines produce neurotransmitters just like your brain. When stress alters your gut microbiota, it can disrupt this communication, potentially affecting your mood and overall health.
How Stress Affects Your Gut
Stress can wreak havoc on your digestive system in several ways. Understanding these can help you identify and address potential issues.
Stress-Induced Digestion Changes
When you’re stressed, your body enters a fight-or-flight mode, diverting energy away from non-essential functions like digestion. This can lead to a host of digestive issues such as bloating, diarrhea, or constipation. Stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline impact the functioning of your gastrointestinal tract, leading to an imbalance.
Impact on Gut Permeability
Chronic stress may increase intestinal permeability, often referred to as ‘leaky gut.’ This condition allows toxins and bacteria to pass into your bloodstream, potentially causing inflammation and affecting your immune system. Understanding and managing stress is crucial to maintaining the integrity of your gut lining.
Alteration of Gut Microbiota
Stress can also alter the composition and function of your gut microbiota. When these beneficial bacteria are disrupted, it can impact your digestion, immune health, and even mood. Stress tends to reduce the diversity of your gut bacteria, which is essential for maintaining a healthy gut environment.
Gastrointestinal Disorders Linked to Stress
Stress can exacerbate existing gastrointestinal disorders or even spark new ones. Knowing this can help you better manage your health.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
IBS is a common gastrointestinal disorder that is often aggravated by stress. The symptoms—such as abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits—can worsen with stress. Learning relaxation techniques and lifestyle changes can be beneficial for managing IBS.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
While IBD, which includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, involves chronic inflammation of the digestive tract, stress can exacerbate the symptoms. Managing stress effectively may help reduce flare-ups and improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from this disorder.
Functional Dyspepsia
Also known as indigestion, functional dyspepsia can be triggered by stress. Symptoms like fullness, nausea, and stomach pain may increase in intensity during stressful times. Understanding your stress triggers and finding ways to deal with them can help alleviate these symptoms.
Coping Mechanisms for Stress-Related Gut Issues
Finding strategies to manage stress can have profound effects on your gut health. While stress is unavoidable, how you cope with it can make all the difference.
Mindfulness and Meditation
Practicing mindfulness and meditation can significantly reduce stress levels and positively impact gut health. These practices encourage you to focus on the present moment, helping you manage anxiety and stress more effectively.
Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular physical activity is a natural stress reliever. Exercise promotes healthy digestion and stimulates the production of endorphins, which enhance your mood and reduce stress.
Diet and Nutrition
Eating a balanced diet rich in fiber, probiotics, and essential nutrients can support a healthy gut. Consider incorporating foods like yogurt, kefir, and fiber-rich fruits and vegetables to promote gut health, especially during stressful periods.
Adequate Sleep
Sleep is vital for stress management and overall well-being. Poor sleep can exacerbate stress and contribute to gut issues, so prioritizing a regular sleep schedule can be beneficial.
Building Social Connections
Having a support network can buffer against stress. Engaging with friends, family, or support groups can help you process emotions and alleviate stress.
Dietary Considerations for Gut Health
How you nourish your body can profoundly affect how your gut responds to stress. Making informed dietary choices can support gut health and promote resilience against stress-induced changes.
Probiotics and Prebiotics
Incorporating probiotics and prebiotics into your diet can help maintain the balance of beneficial bacteria in your gut. Probiotics are live bacteria found in foods like yogurt and fermented foods, while prebiotics are fibers found in foods such as bananas and asparagus that feed these bacteria.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon and sardines, have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce gut inflammation. Including these in your diet may protect against stress-related gut disturbances.
Hydration
Adequate hydration is crucial for digestion and can help prevent stress-induced digestive complications. Ensure you’re drinking enough water throughout the day to support your digestive system.
Understanding Psychological Interventions
Sometimes, managing stress requires assistance beyond lifestyle changes. Various psychological interventions can offer support and relief.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT helps you identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to stress. By working with a therapist, you can develop effective coping strategies to manage stress and its impact on your gut health.
Stress Management Techniques
Learning stress management techniques such as progressive muscle relaxation, breathing exercises, and guided imagery can significantly impact your ability to handle stress. These techniques are tools to keep stress from overwhelming you and affecting your gut.
Counseling and Support Groups
Joining support groups or seeking counseling can be particularly beneficial if stress is related to specific life events or circumstances. Talking to a professional can provide perspective and practical solutions.
When to Seek Medical Advice
While stress-related gut issues are common, persistent symptoms might require medical attention. Knowing when to seek professional help is crucial for your well-being.
Persistent Symptoms
If you experience prolonged digestive symptoms that do not improve with lifestyle changes, it might be time to consult a healthcare professional. Early intervention can prevent further complications.
Changes in Bowel Habits
Noticeable changes in bowel habits, such as severe constipation, diarrhea, or blood in stools, should prompt a visit to your doctor. These could indicate underlying conditions that need medical attention.
Severe Abdominal Pain
Severe or persistent abdominal pain should never be ignored. This could indicate a serious condition that requires immediate medical evaluation.
Conclusion
Understanding the connection between stress and gut health can empower you to make informed decisions about your well-being. By recognizing how stress impacts your gut, you can take proactive steps to manage stress and maintain a healthy digestive system. Remember, your mental and physical health are closely intertwined, and caring for your mind is equally important as caring for your body.