From Diet to Disease: Understanding the Factors Behind Fatty Liver
Introduction
Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition in which excess fat builds up in the liver. This can lead to inflammation and damage to the liver cells, ultimately affecting the organ’s ability to function properly. Fatty liver disease is becoming increasingly common, with an estimated 25% of adults worldwide affected by the condition. While the exact causes of fatty liver disease are not fully understood, there are several risk factors that have been identified, including diet, obesity, and certain medical conditions. In this article, we will explore the factors behind fatty liver disease, with a particular focus on the role of diet in the development of the condition.
Understanding Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease is categorized into two main types: non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcoholic fatty liver disease. NAFLD is the most common form of the condition and is not related to alcohol consumption. It is often associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome. Alcoholic fatty liver disease, on the other hand, is caused by excessive alcohol consumption and is characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver due to the toxic effects of alcohol.
Both types of fatty liver disease can progress to more serious conditions, such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which is characterized by inflammation and liver cell damage, and can eventually lead to cirrhosis or liver cancer. Therefore, it is important to understand the factors that contribute to the development of fatty liver disease in order to prevent its progression and complications.
The Role of Diet in Fatty Liver Disease
Diet plays a crucial role in the development and progression of fatty liver disease. A diet high in saturated fats, trans fats, and sugar can lead to the accumulation of fat in the liver, as these nutrients are easily converted into triglycerides, which are stored in the liver as fat. Additionally, excessive calorie consumption can also contribute to the development of fatty liver disease, as the liver is unable to process and metabolize the excess energy, leading to the buildup of fat.
In addition to the type and amount of nutrients consumed, the timing of meals can also impact the development of fatty liver disease. Studies have shown that irregular meal patterns, such as skipping meals or eating late at night, can disrupt the body’s metabolism and increase the risk of developing NAFLD. This is because the liver plays a key role in regulating the body’s energy balance and metabolism, and disruptions in its function can lead to the accumulation of fat in the liver.
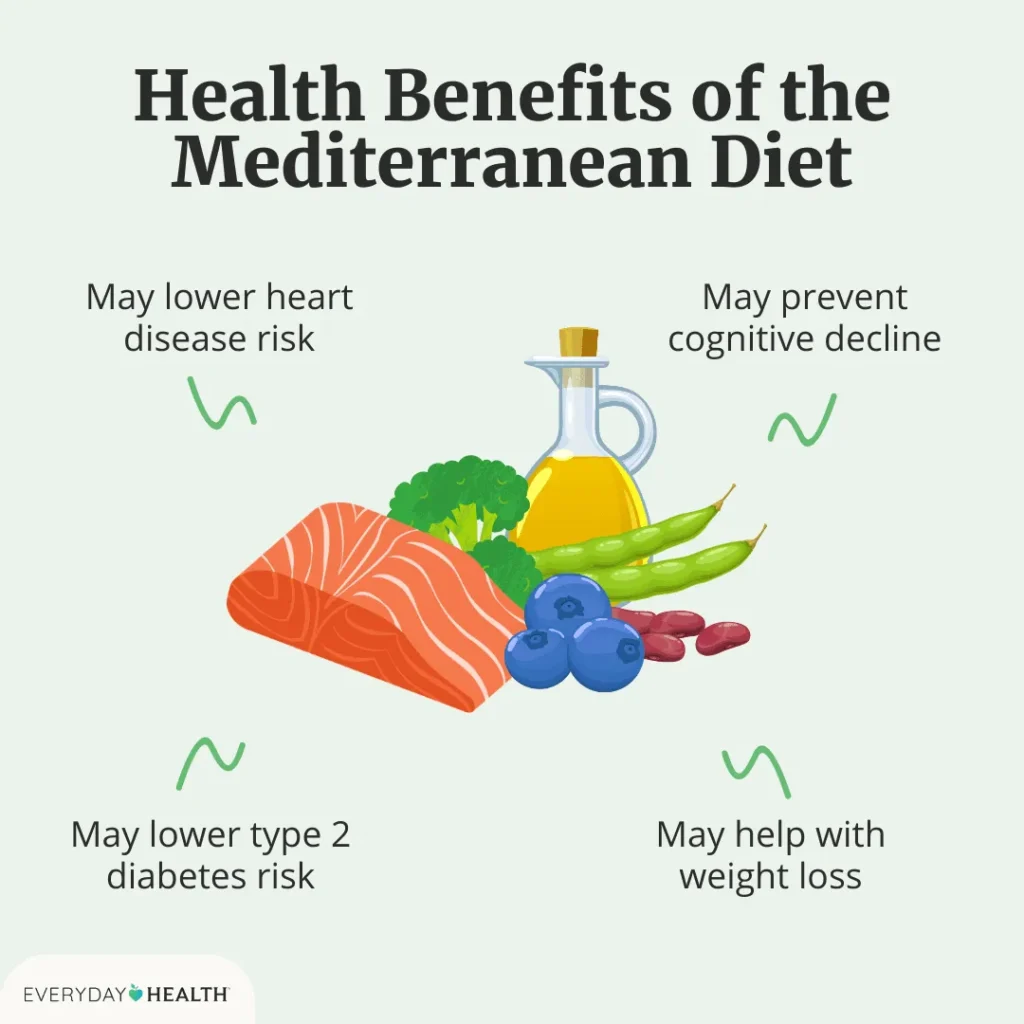
Furthermore, certain dietary patterns, such as the Western diet, which is high in processed foods, red meat, and sugary beverages, have been associated with an increased risk of developing fatty liver disease. On the other hand, a Mediterranean-style diet, which is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, has been shown to have a protective effect against the condition. This is because the nutrients found in a Mediterranean-style diet can help to reduce inflammation, improve insulin sensitivity, and promote the metabolism of fats in the liver.
Other Factors Contributing to Fatty Liver Disease
While diet plays a significant role in the development of fatty liver disease, there are other factors that can contribute to the condition as well. Obesity is a major risk factor for NAFLD, as excess body fat can lead to insulin resistance and inflammation, both of which can contribute to the accumulation of fat in the liver. Insulin resistance, in particular, is a key factor in the development of NAFLD, as it impairs the liver’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels and metabolize fats.
In addition to obesity and insulin resistance, certain medical conditions can also increase the risk of developing fatty liver disease. These conditions include type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, and metabolic syndrome, all of which are characterized by abnormalities in metabolism and can lead to the accumulation of fat in the liver. Genetic factors may also play a role in the development of fatty liver disease, as some individuals may be more predisposed to the condition due to their genetic makeup.
Preventing and Treating Fatty Liver Disease
Preventing and treating fatty liver disease involves making lifestyle changes that can help to reduce the buildup of fat in the liver and improve liver function. One of the most important steps in preventing fatty liver disease is maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help to reduce the risk of developing NAFLD, while regular physical activity can help to improve insulin sensitivity and promote the metabolism of fats in the liver.
In addition to diet and exercise, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption is also important in preventing alcoholic fatty liver disease. Limiting alcohol intake to no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men can help to reduce the risk of developing the condition. For individuals with NAFLD, avoiding foods high in saturated fats, trans fats, and sugar, and instead opting for a Mediterranean-style diet, can help to improve liver function and reduce inflammation.
For individuals with more advanced stages of fatty liver disease, such as NASH or cirrhosis, medical treatment may be necessary to manage the condition and prevent further complications. This may include medications to reduce inflammation and improve liver function, as well as lifestyle interventions, such as weight loss and exercise, to improve overall health. In some cases, liver transplantation may be needed for individuals with end-stage liver disease.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can fatty liver disease be reversed?
A: In the early stages, fatty liver disease can be reversed through lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise. However, once the condition has progressed to more severe stages, such as NASH or cirrhosis, it may be more difficult to reverse the damage to the liver.
Q: Is fatty liver disease hereditary?
A: While genetic factors may play a role in the development of fatty liver disease, the condition is not purely hereditary. Lifestyle factors, such as diet and exercise, also play a significant role in the development of the condition.
Q: Are there any medications that can treat fatty liver disease?
A: There are no specific medications approved for the treatment of fatty liver disease. However, medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms, such as inflammation and insulin resistance, in individuals with more advanced stages of the condition.
Q: Can fatty liver disease lead to liver cancer?
A: In some cases, fatty liver disease can progress to liver cancer, particularly in individuals with more advanced stages of the condition, such as NASH or cirrhosis. It is important to monitor the condition and seek medical treatment if necessary to prevent further complications.
Conclusion
Fatty liver disease is a common condition that can have serious consequences if left untreated. While the exact causes of the condition are not fully understood, there are several risk factors that have been identified, including diet, obesity, and certain medical conditions. By making lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise, individuals can reduce their risk of developing fatty liver disease and improve liver function. It is important to seek medical advice if you are concerned about your liver health, as early detection and treatment can help to prevent the progression of the condition and reduce the risk of complications.