If you haven't heard of C. diff before, it's a bacterial infection in the colon caused by the bacterium Clostridioides difficile. These bacterial spores are all around in the environment, making it easy for them to be transferred into your colon through your mouth. C. diff is an aggressive bacterium that causes serious problems, affecting nearly half a million people in the United States each year and resulting in thousands of deaths annually. Women are more likely than men to get a C. diff infection, although the reason for this is still unknown. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment of C. diff infection, as well as the risk factors and prevention methods.
Overview of C. Diff Infection
C. diff infection, also known as Clostridioides difficile infection, is a bacterial infection that affects the colon. It is caused by the bacterium Clostridioides difficile, which can be found in various environments, including healthcare settings and non-healthcare settings. While the bacterium is present in the environment, infection only occurs when the spores are able to grow in the colon. C. diff infection is a significant health concern, affecting nearly half a million people in the United States each year and causing approximately 30,000 deaths annually. It is more common in women, although the reason for this is still unknown.
Transmission and Prevention
C. diff infection can be transmitted through the ingestion of C. diff spores. These spores can be found on objects in the environment or on the skin of individuals who are carrying the bacterium. If you touch an object contaminated with C. diff and then bring your hand to your mouth, you can introduce the bacterium into your gastrointestinal system. Prevention methods and strategies are important in reducing the risk of transmission. These include practicing good hand hygiene by washing hands with soap and water, especially after using the bathroom and before eating or drinking. It is also important for healthcare workers to wash their hands before touching patients. Additionally, cleaning and disinfecting commonly touched surfaces with a bleach-based cleaner can help prevent the spread of C. diff.

Manifestation in the Body
C. diff infection primarily affects the gastrointestinal system. The bacterium grows and multiplies in the colon, releasing toxins that cause damage to the colon lining. This damage results in symptoms such as diarrhea, stomach pain, cramping, nausea, loss of appetite, abdominal swelling, fever, rapid heart rate, and blood in the stool. C. diff infection can also have an impact on the gut microbiome, which is the community of bacteria in the colon that helps maintain a healthy digestive system. The overgrowth of C. diff can disrupt the balance of the gut microbiome, leading to further complications.
Risk Factors
There are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing a C. diff infection. These include taking antibiotics for another infection, being in a nursing home or hospital, having a weakened immune system, having a bowel disease, taking acid-suppressing medications unnecessarily, having a history of C. diff infections, and being 65 years of age or older. It is important to note that anyone can be at risk of developing a C. diff infection, even without any of the known risk factors.
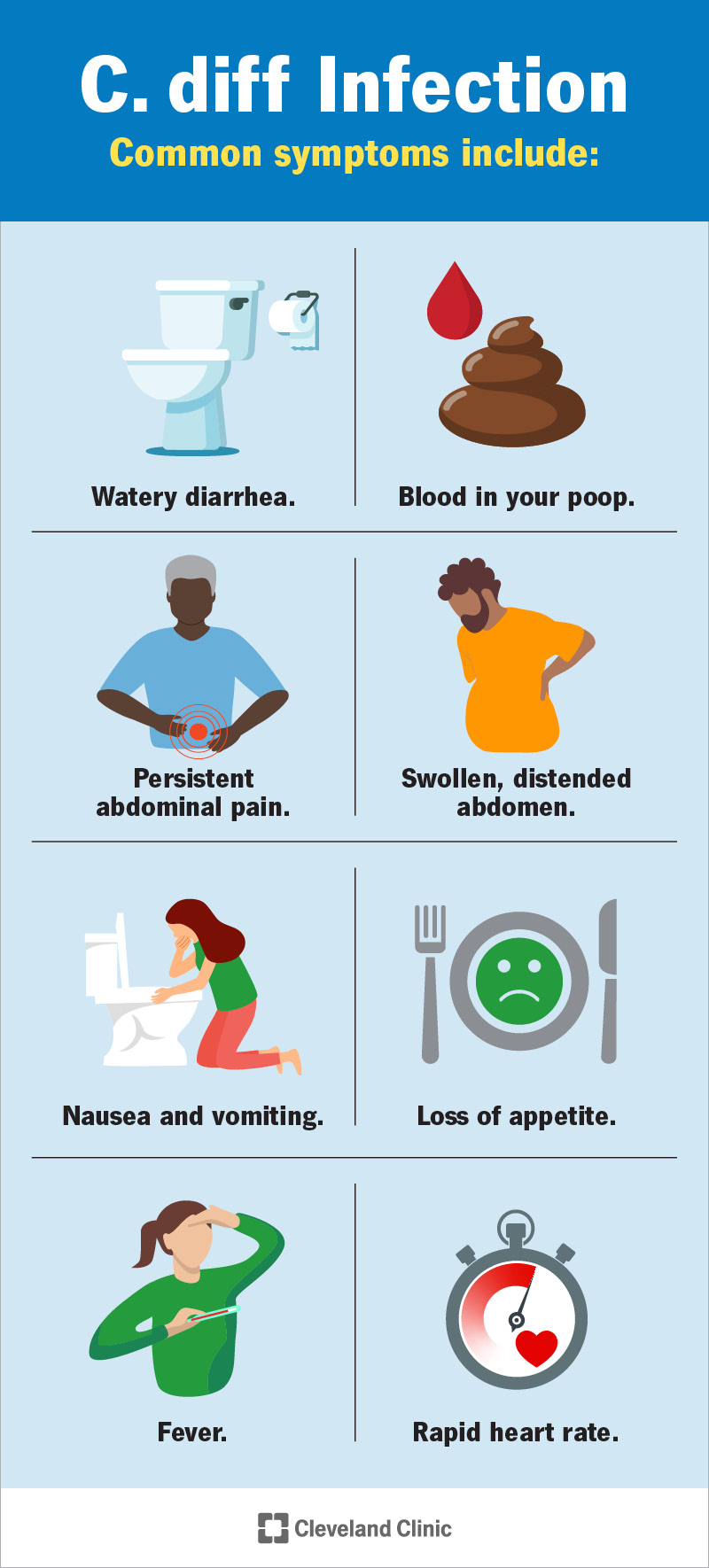
Symptoms
Common symptoms associated with C. diff infection include diarrhea, stomach pain, cramping, nausea, loss of appetite, abdominal swelling, fever, rapid heart rate, and blood in the stool. These symptoms may initially be mild, resembling a gastrointestinal illness, but can worsen over time. One distinctive characteristic of C. diff infection is the presence of a strong odor in the stool. It is essential to seek medical attention if these symptoms persist or worsen, as prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial.
Diagnosis
The process of diagnosing C. diff infection typically involves collecting a stool specimen for laboratory examination. Laboratory tests can detect the presence of C. diff toxins in the stool, confirming the infection. In severe cases or if the initial diagnosis is inconclusive, blood tests and imaging tests such as X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or a colonoscopy may be used to assess the extent of colon damage and to rule out other potential causes of symptoms.

Treatment
Initial treatment strategies for C. diff infection may involve stopping the use of antibiotics that may have caused the infection, especially if the illness is mild. Antibiotics that specifically target C. diff bacteria, such as vancomycin, fidaxomicin, and metronidazole (for mild infections only), may be prescribed. It is essential to complete the entire course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve, to ensure the complete eradication of the infection and prevent recurrence. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to administer intravenous antibiotics and fluids.
Novel Treatments
Microbiome-based treatments have recently been approved by the FDA as alternative options for the prevention of recurrent C. diff infections. These treatments involve the introduction of beneficial bacteria into the gastrointestinal system to restore a healthy gut microbiome. The efficacy and approval status of these treatments may vary, and they should be discussed with healthcare providers to determine the most suitable treatment approach.

Recovery and Recurrence
Signs of recovery from C. diff infection include the resolution of symptoms and a return to normal bowel movements. However, it is important to note that recurrence of C. diff infection is possible. Up to 1 in 4 people who have had a C. diff infection may experience a relapse or subsequent infections. It is crucial to stay vigilant and promptly report any symptoms to healthcare providers.
Proactive Steps Post-Infection
After recovering from a C. diff infection, there are proactive steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of recurrence and promote overall health. These steps include practicing good personal hygiene, such as regular handwashing with soap and water, especially before meals and after using the bathroom. Communication with healthcare providers is also important, as they can provide guidance on preventive measures and monitor for any potential signs of recurrent infection. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can support the overall well-being of individuals post-infection.
In conclusion, C. diff infection is a significant health concern that affects a large number of individuals each year. It is important to understand the transmission, prevention, manifestation, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of C. diff infection to promote prompt diagnosis, effective management, and proactive steps to reduce the risk of recurrence. By taking preventive measures, seeking timely medical attention, and following prescribed treatment regimens, individuals can minimize the impact of C. diff infection on their health and well-being.

Source: https://www.healthywomen.org/your-health/c-diff-infection