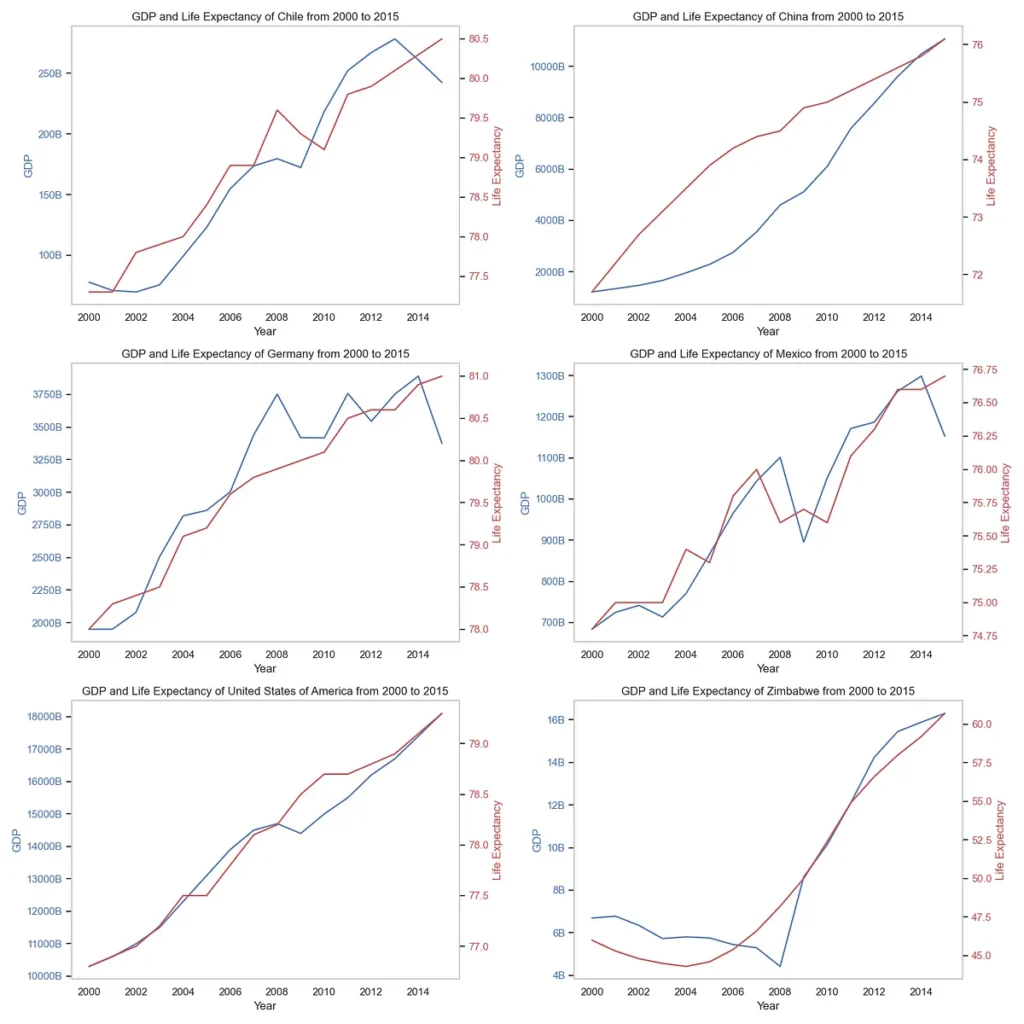
Life expectancy is a key indicator of a population’s overall health and well-being. It is influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, lifestyle, access to healthcare, and socio-economic status. In recent years, researchers have been studying the disparities in life expectancy across different demographics to better understand why some groups of people live longer than others.
Factors Affecting Life Expectancy
There are several factors that can influence life expectancy, including:
- Genetics: Some people are genetically predisposed to certain health conditions that can affect their life expectancy.
- Lifestyle: Factors such as diet, exercise, smoking, and alcohol consumption can have a significant impact on life expectancy.
- Access to Healthcare: People who have access to quality healthcare are more likely to receive timely medical treatment and preventive care, which can help them live longer.
- Socio-Economic Status: Income level, education, and employment status can also influence life expectancy. People with higher socio-economic status tend to live longer than those with lower socio-economic status.
Racial and Ethnic Disparities
One of the most significant disparities in life expectancy is seen among different racial and ethnic groups. Studies have shown that African Americans have a lower life expectancy compared to white Americans. This disparity is often attributed to factors such as poverty, discrimination, and limited access to healthcare among African Americans.
Similarly, Hispanic Americans have been found to have a longer life expectancy compared to non-Hispanic whites. This is believed to be due to cultural factors, such as diet and close family ties, that contribute to better health outcomes among Hispanic Americans.
Gender Disparities
Gender also plays a role in life expectancy. Women tend to live longer than men, with the gap in life expectancy between men and women varying across different countries and populations. Biological factors, such as hormonal differences, are thought to contribute to women’s longer life expectancy. Additionally, men are more likely to engage in risky behaviors, such as smoking and heavy drinking, which can negatively impact their health and life expectancy.
Income Disparities
Income level is a major determinant of life expectancy. People with higher income levels tend to live longer than those with lower income levels. This is because individuals with higher incomes are more likely to have access to quality healthcare, nutritious food, safe housing, and other resources that contribute to better health outcomes.
Additionally, people with higher incomes are more likely to engage in healthy behaviors, such as regular exercise and preventive healthcare, which can help them live longer.
Geographic Disparities
Life expectancy can also vary significantly based on geographic location. Studies have shown that people living in urban areas tend to have longer life expectancies compared to those living in rural areas. This is often attributed to better access to healthcare, higher socio-economic status, and healthier lifestyle choices in urban areas.
Furthermore, life expectancy can vary among different regions and countries. For example, people in developed countries tend to have longer life expectancies compared to those in developing countries. This is due to differences in healthcare infrastructure, socio-economic development, and public health policies.
Conclusion
Exploring the disparities in life expectancy across different demographics is crucial for identifying the underlying factors that contribute to these disparities. By understanding why certain groups of people live longer than others, policymakers and healthcare providers can develop targeted interventions to improve health outcomes and reduce disparities in life expectancy.
Addressing issues such as poverty, discrimination, access to healthcare, and healthy lifestyle choices can help narrow the gap in life expectancy among different demographics and improve overall population health.
#Exploring #Disparities #Life #Expectancy #Demographics