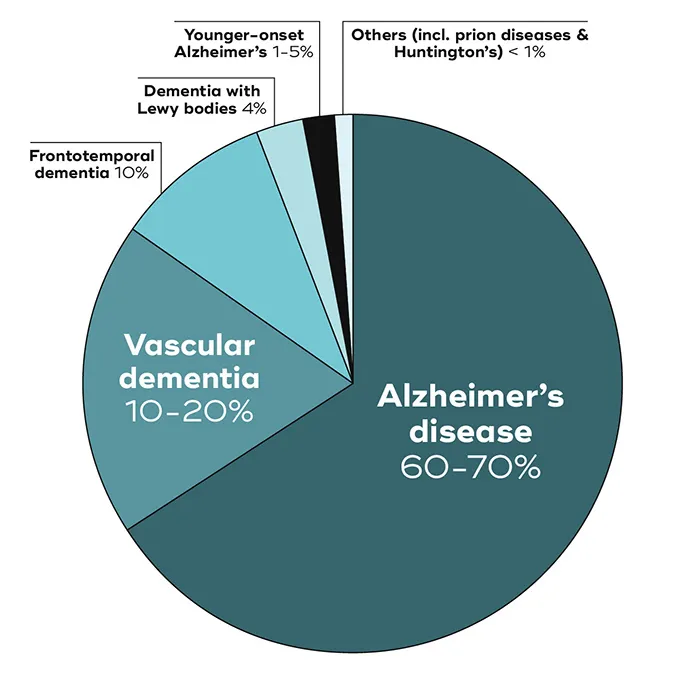
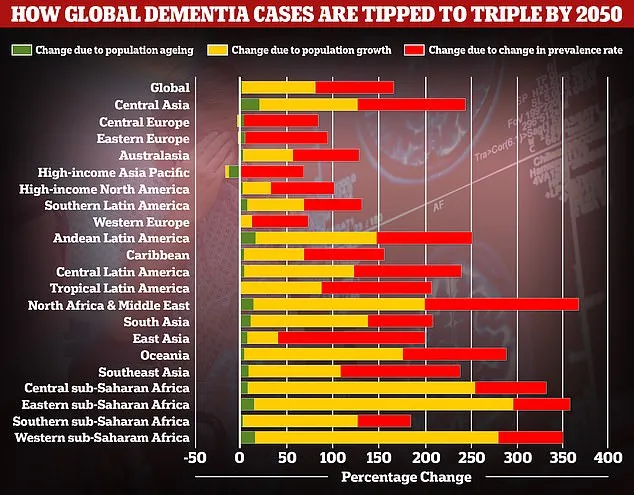
In a recent study published in the Journal of Neurology, researchers have uncovered shocking disparities in dementia rates across different countries. The study, which analyzed data from over 20 countries, found that the prevalence of dementia varies significantly from one country to another, with some countries reporting much higher rates than others.
Understanding the Impact of Dementia
Dementia is a progressive neurological condition that affects memory, cognitive function, and behavior. It is estimated that over 50 million people worldwide are living with dementia, and this number is expected to triple by 2050. Dementia not only has a significant impact on the individuals affected but also on their families, caregivers, and healthcare systems.
The Study Findings
The study revealed that Japan has the highest prevalence of dementia, with over 15% of the population aged 65 and older affected. This is significantly higher than the global average of around 8%. On the other hand, countries like Nigeria and India have much lower rates of dementia, with less than 2% of the population affected.
These findings have raised important questions about the factors that contribute to these disparities. The researchers found that socio-economic factors, such as education level, income, and access to healthcare, play a significant role in determining dementia rates. Countries with higher levels of education and income tend to have lower rates of dementia, while those with lower socio-economic status are more likely to experience higher rates of the condition.
Implications for Global Health
The study has important implications for global health policy and planning. As the global population ages, the burden of dementia is expected to increase, placing a significant strain on healthcare systems around the world. Understanding the factors that contribute to disparities in dementia rates is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
One of the key recommendations from the study is the need for targeted interventions in countries with high rates of dementia. This could include initiatives to improve access to education and healthcare, as well as raising awareness about the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle to prevent dementia.
Conclusion
The study revealing shocking disparities in dementia rates across different countries highlights the urgent need for action to address this growing global health challenge. By understanding the factors that contribute to these disparities, policymakers and healthcare providers can develop targeted interventions to prevent and treat dementia effectively.
As the global population continues to age, it is essential that we prioritize the health and well-being of individuals affected by dementia and work towards creating a more inclusive and supportive society for all.
#Study #Reveals #Shocking #Disparities #Dementia #Rates #Countries