Uncovering the Hidden Dangers: The Most Common Causes of Fatty Liver
Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition in which excess fat builds up in the liver. This can lead to inflammation and damage to the liver, potentially progressing to more serious conditions such as cirrhosis and liver cancer. Fatty liver disease is becoming increasingly common, with an estimated 25% of the global population affected by the condition. In this article, we will explore the most common causes of fatty liver disease and how you can protect yourself from this potentially dangerous condition.
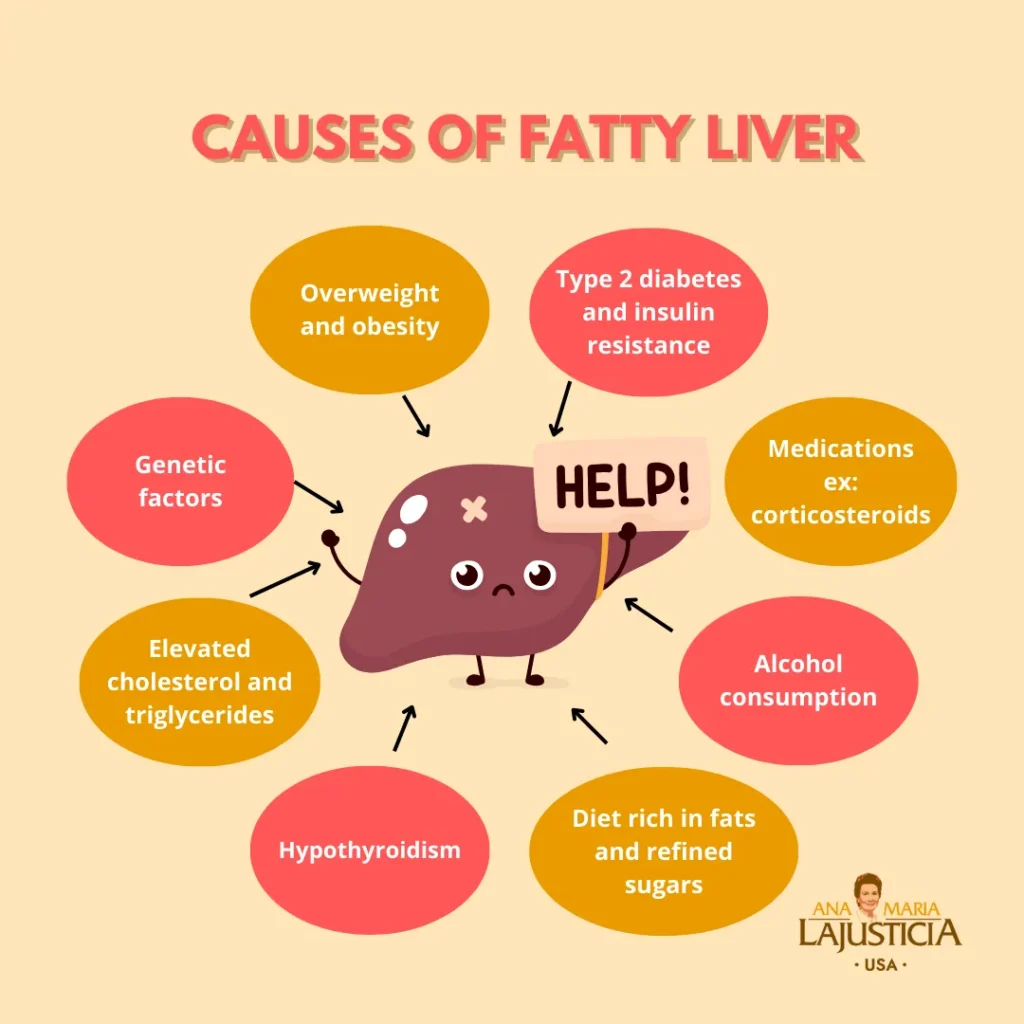
1. Obesity
One of the leading causes of fatty liver disease is obesity. When you consume more calories than your body can burn, the excess calories are stored as fat in the liver. Over time, this can lead to the development of fatty liver disease. People who are obese or overweight are at a higher risk of developing fatty liver disease, as their bodies are more likely to store excess fat in the liver.
2. Insulin resistance
Insulin resistance is a condition in which the body’s cells become resistant to the effects of insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. When the body becomes insulin resistant, it may produce more insulin to compensate, which can lead to an increase in fat production in the liver. This excess fat can accumulate in the liver and lead to fatty liver disease. Insulin resistance is commonly seen in people with type 2 diabetes, but it can also occur in individuals who are overweight or sedentary.
3. High cholesterol and triglycerides
High levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood can also contribute to the development of fatty liver disease. When there is an excess of these fats in the blood, they can be deposited in the liver, leading to the accumulation of fat in the liver cells. This can cause inflammation and damage to the liver, increasing the risk of developing fatty liver disease. People with high cholesterol or triglyceride levels should work with their healthcare provider to manage their levels and reduce their risk of developing fatty liver disease.
4. Poor diet
A diet high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can also contribute to the development of fatty liver disease. These types of foods are often high in calories and low in nutrients, leading to weight gain and an increase in fat accumulation in the liver. Consuming a diet that is high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help reduce your risk of developing fatty liver disease. Avoiding processed foods, sugary drinks, and fried foods can also help protect your liver health.
5. Alcohol consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption is a well-known cause of fatty liver disease. When you consume alcohol, your liver works to metabolize it and break it down. However, excessive alcohol consumption can overwhelm the liver, leading to the accumulation of fat in the liver cells. Over time, this can lead to inflammation, scarring, and liver damage. It is important to drink alcohol in moderation and to seek help if you are struggling with alcohol abuse or dependency.
6. Sedentary lifestyle
A sedentary lifestyle, in which you are not getting enough physical activity, can also contribute to the development of fatty liver disease. Physical activity helps to burn calories and reduce fat accumulation in the liver. People who are inactive are more likely to be overweight or obese, increasing their risk of developing fatty liver disease. Incorporating regular exercise into your routine can help protect your liver health and reduce your risk of fatty liver disease.
7. Genetics
Genetics can also play a role in the development of fatty liver disease. Some people may be more predisposed to developing the condition due to their genetic makeup. If you have a family history of fatty liver disease, you may be at a higher risk of developing the condition yourself. It is important to be aware of your family history and to work with your healthcare provider to monitor your liver health and reduce your risk of developing fatty liver disease.
Protecting Yourself from Fatty Liver Disease
While fatty liver disease is a common and potentially dangerous condition, there are steps you can take to protect yourself and reduce your risk of developing the disease. Here are some tips for maintaining a healthy liver and reducing your risk of fatty liver disease:
1. Maintain a healthy weight: One of the most important ways to protect your liver health is to maintain a healthy weight. If you are overweight or obese, losing weight can help reduce fat accumulation in the liver and improve liver function. Aim to achieve a healthy weight through a combination of a healthy diet and regular exercise.
2. Eat a healthy diet: Consuming a diet that is high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help protect your liver health. Avoiding processed foods, sugary drinks, and fried foods can also help reduce your risk of developing fatty liver disease. Be mindful of your calorie intake and aim to eat a balanced diet that is rich in nutrients.
3. Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption is a leading cause of fatty liver disease. If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation and be mindful of your consumption. Men should limit their alcohol intake to no more than two drinks per day, while women should limit their alcohol intake to no more than one drink per day.
4. Exercise regularly: Physical activity is essential for maintaining a healthy liver and reducing your risk of fatty liver disease. Aim to incorporate at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise into your routine each week. This can include activities such as walking, cycling, swimming, or dancing.
5. Manage chronic conditions: If you have conditions such as diabetes, high cholesterol, or high blood pressure, it is important to work with your healthcare provider to manage these conditions and reduce your risk of developing fatty liver disease. Follow your provider’s recommendations for monitoring your condition and taking any necessary medications.
6. Get regular check-ups: Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help monitor your liver health and catch any potential issues early. Your provider may recommend blood tests or imaging studies to assess your liver function and screen for fatty liver disease. Be proactive about your health and follow your provider’s recommendations for monitoring your liver health.
7. Avoid crash diets: Crash diets or rapid weight loss can actually be harmful to your liver health. These types of diets can lead to a rapid breakdown of fat in the liver, which can cause inflammation and liver damage. Instead, focus on making gradual, sustainable changes to your diet and exercise routine to achieve long-term success.
FAQs
Q: Can fatty liver disease be reversed?
A: In many cases, fatty liver disease can be reversed with lifestyle changes such as weight loss, a healthy diet, and regular exercise. However, it is important to work with your healthcare provider to monitor your liver health and make necessary changes to protect your liver.
Q: Is fatty liver disease dangerous?
A: Fatty liver disease can be dangerous if left untreated. It can progress to more serious conditions such as cirrhosis and liver cancer. It is important to take steps to protect your liver health and reduce your risk of developing fatty liver disease.
Q: How is fatty liver disease diagnosed?
A: Fatty liver disease is typically diagnosed through blood tests, imaging studies such as ultrasound or MRI, and sometimes a liver biopsy. Your healthcare provider may recommend these tests if they suspect you have fatty liver disease based on your symptoms or risk factors.
Q: Is fatty liver disease hereditary?
A: While genetics can play a role in the development of fatty liver disease, it is not always hereditary. Some people may be more predisposed to developing the condition due to their genetic makeup, but lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and alcohol consumption also play a significant role.
Q: Can fatty liver disease be prevented?
A: Fatty liver disease can often be prevented by maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, limiting alcohol consumption, exercising regularly, and managing chronic conditions such as diabetes and high cholesterol. By taking steps to protect your liver health, you can reduce your risk of developing fatty liver disease.
In conclusion, fatty liver disease is a common and potentially dangerous condition that can be caused by a variety of factors, including obesity, insulin resistance, high cholesterol, poor diet, alcohol consumption, sedentary lifestyle, and genetics. By taking steps to protect your liver health, such as maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, limiting alcohol consumption, exercising regularly, and managing chronic conditions, you can reduce your risk of developing fatty liver disease. If you suspect you may have fatty liver disease, it is important to work with your healthcare provider to monitor your liver health and make necessary changes to protect your liver. By being proactive about your health and taking steps to protect your liver, you can reduce your risk of developing fatty liver disease and maintain a healthy liver for years to come.