Unlocking the Link Between Metabolic Health and Liver Function
Introduction
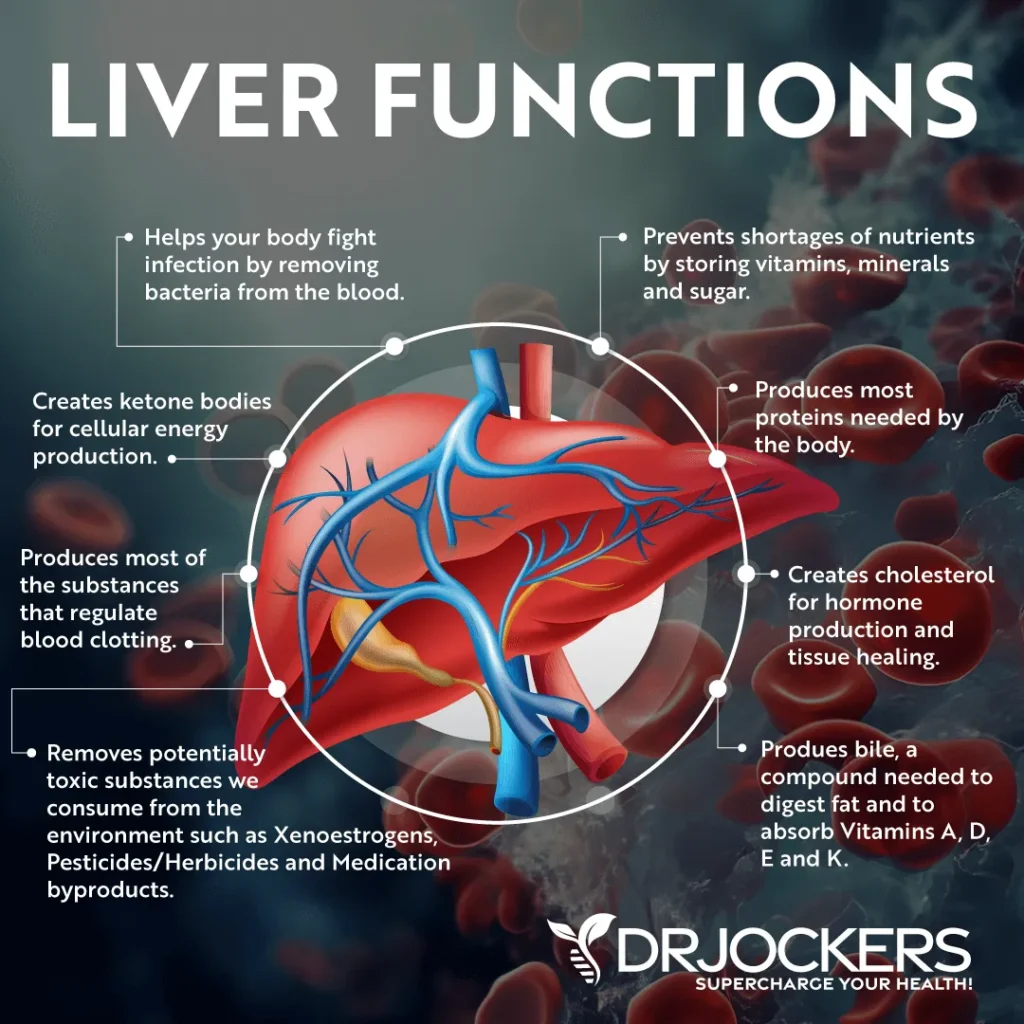
The liver is a vital organ in the human body, responsible for a variety of functions such as detoxification, metabolism, and storage of nutrients. Metabolic health, on the other hand, refers to the overall health of the body’s metabolism, including how well the body processes and utilizes nutrients. Recent research has shown a strong link between metabolic health and liver function, with poor metabolic health often leading to liver dysfunction. In this article, we will explore the connection between metabolic health and liver function, and how improving one can positively impact the other.
The Role of the Liver in Metabolic Health
The liver plays a crucial role in maintaining metabolic health by regulating glucose and lipid metabolism. Glucose is the primary source of energy for the body, and the liver plays a key role in maintaining blood glucose levels within a narrow range. It does this by storing excess glucose as glycogen for later use or converting it into fat for storage. The liver also plays a role in breaking down fats and producing cholesterol, which is essential for the production of hormones and cell membranes.
When the liver is functioning properly, it helps to maintain a healthy metabolic balance in the body. However, when the liver becomes compromised due to factors such as poor diet, obesity, or excessive alcohol consumption, it can lead to metabolic imbalances that can contribute to the development of metabolic disorders such as diabetes, fatty liver disease, and metabolic syndrome.
The Link Between Metabolic Health and Liver Function
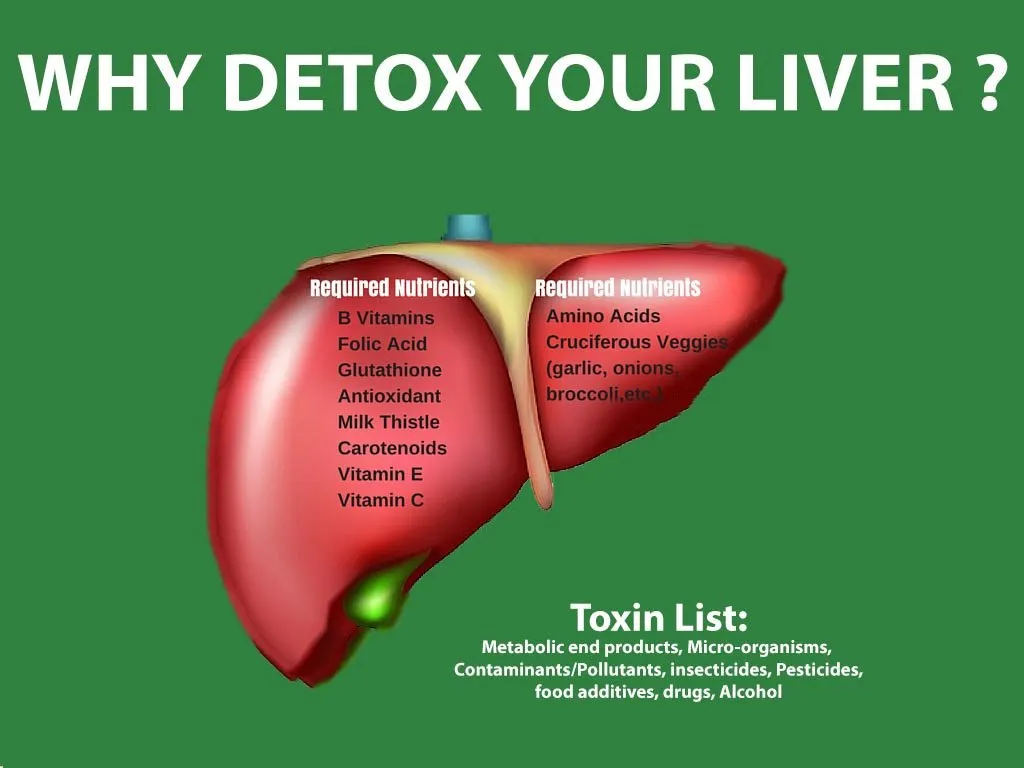
Research has shown that there is a strong link between metabolic health and liver function. Poor metabolic health, characterized by insulin resistance, obesity, and high levels of inflammation, can lead to liver dysfunction. This is because when the body is unable to properly process and utilize nutrients, it can lead to an accumulation of fat in the liver, a condition known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). NAFLD is the most common liver disorder in the Western world, affecting up to 25% of the population.
NAFLD is a progressive disease that can lead to more serious liver conditions such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cirrhosis, and liver cancer. It is also closely linked to metabolic disorders such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease. In fact, individuals with NAFLD are at a higher risk of developing these conditions compared to those without liver dysfunction.
Improving Metabolic Health to Support Liver Function
The good news is that improving metabolic health can positively impact liver function. Lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and weight management play a key role in supporting both metabolic health and liver function. Here are some strategies to improve metabolic health and support liver function:
1. Eat a healthy diet: A diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help support liver function and improve metabolic health. Avoiding processed foods, sugary beverages, and trans fats can also help reduce the risk of liver dysfunction.
2. Exercise regularly: Physical activity has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and support liver function. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as walking, cycling, or swimming.
3. Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity is a major risk factor for both metabolic disorders and liver dysfunction. Losing weight through a combination of diet and exercise can help improve both metabolic health and liver function.
4. Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can damage the liver and contribute to the development of liver diseases such as fatty liver disease and cirrhosis. Limit alcohol intake to no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men.
5. Manage stress: Chronic stress can negatively impact metabolic health and liver function. Practicing stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help improve both.
FAQs
Q: Can poor metabolic health cause liver disease?
A: Yes, poor metabolic health, characterized by insulin resistance, obesity, and inflammation, can lead to the development of liver diseases such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
Q: What are the symptoms of liver dysfunction?
A: Symptoms of liver dysfunction can vary depending on the underlying condition, but common symptoms include fatigue, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), abdominal pain, and swelling of the abdomen.
Q: Can NAFLD be reversed?
A: Yes, NAFLD can be reversed with lifestyle changes such as diet, exercise, and weight loss. In some cases, medications may also be prescribed to help improve liver function.
Q: How can I improve my metabolic health?
A: To improve metabolic health, focus on eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, limiting alcohol consumption, and managing stress.
Conclusion
In conclusion, there is a strong link between metabolic health and liver function, with poor metabolic health often leading to liver dysfunction. By improving metabolic health through lifestyle changes such as diet, exercise, and weight management, it is possible to support liver function and reduce the risk of developing liver diseases. Taking steps to improve metabolic health can have a positive impact on overall health and well-being.